Ingredients: Pimpinella anisum
Active Ingredients: estrols, estragole,γ-hymachalen, para-anisaldehyde and methyl cavicol, anisaldehyde,coumarins,scopo-letin,umbelliferone,ter hydrocarbons, anethole, Polyenes, polyacetylenes,، α-cuparene ,α-himachalene,flavonoid(apigenin), limonene,p-anisaldehyde
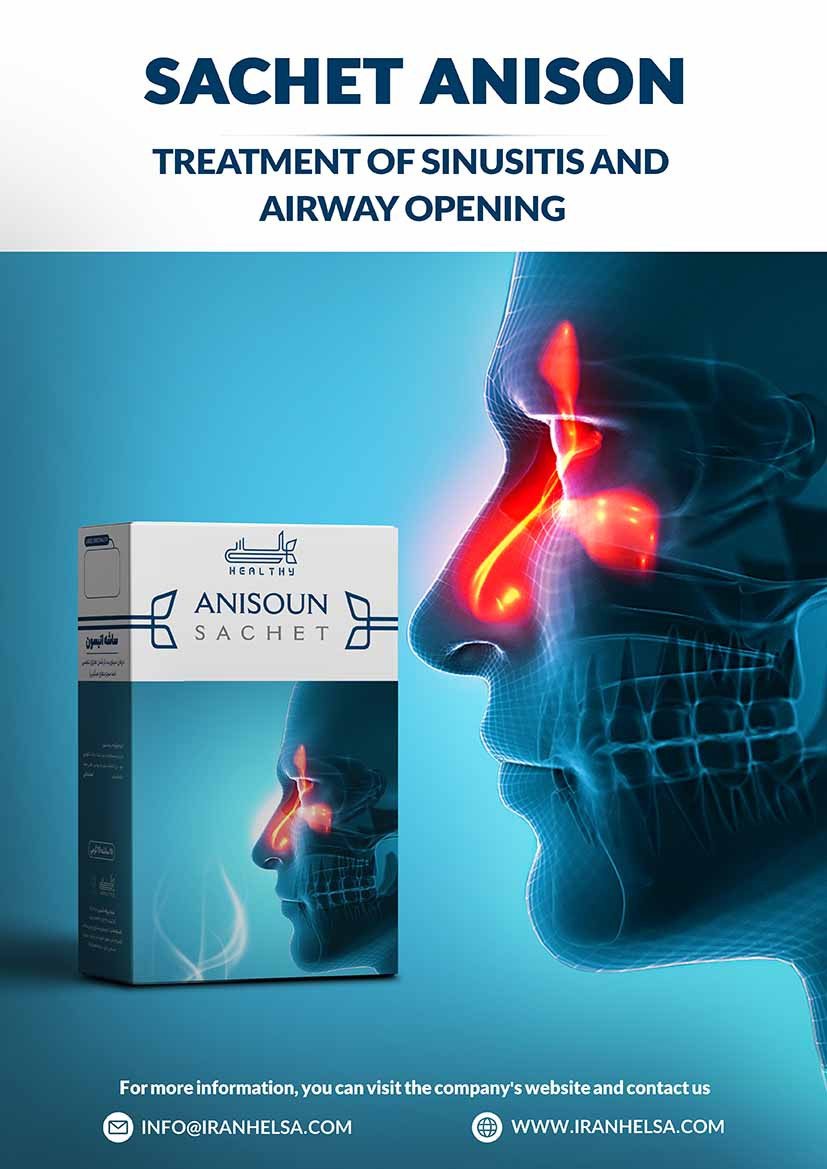
Indications: Smoking it to relieve the headache caused by the cold and to pour cold and wet waste from the brain to the throat and lungs
Dosage and administration: Smoke and inhale half a sachet once a night.(If it is not possible to use the smoking method, you can boil 1 sachet in 2 glasses of water every 8 hours, then steam for 5 to 10 minutes.
Side effects: No specific side effects have been reported
Recommended tips: does not have
Contraindications and precautions: does not have
Pharmacological effects and mechanism of action MOA: aniseed are used as analgesic in migraine.in the nose, activation of nasal fibroblasts induces ECM deposition and remodeling. It can be an important cause of CRSsNP . The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in the stalk part or early stage of a nasal polyp in CRSwNP is involved in the overexpression of a-SMA, fibronectin, and collagen type I as well as the formation of nasal polyps and the cause of CRSwNP . TGF-β1, a representative profibrotic cytokine, has been reported to be a prime stimulator of fibroblast activation and to induce activation and differentiation of fibroblasts into myofibroblasts expressing α-SMA. TGF-β1 promotes massive amounts of ECM deposition, which leads to airway tissue remodeling Apigenin is a bioflavonoid compound, and it affects cellular processes such as cell proliferation, migration, tumor growth, and fibrosis . Ricupero et al. reported that apigenin inhibited the proliferation of myofibroblasts and expression of collagen type I and α-SMA and decreased TGF-β-induced α-SMA expression by inhibiting the Akt pathway in lung fibroblasts . Jun et al. demonstrated that physiological concentrations of apigenin inhibited endothelin-1-induced contraction of collagen gels in an in vitro model of ECM remodeling . In a bleomycin-induced systemic sclerosis mouse model, apigenin suppressed bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis We showed that apigenin has anti-tissue remodeling effects on TGF-β1 stimulated nasal fibroblast and inferior turbinate tissue. TGF-β1 stimulated nasal fibroblasts induced differentiation into myofibroblasts. Differentiated myofibroblasts increased the expression of ECM components such as fibronectin and collagen type I, leading to tissue remodeling. Apigenin partially reduced TGF-β1-induced total collagen expression at concentrations below 5 μM, but did not significantly decrease myofibroblast differentiation and inhibition of ECM components. However, apigenin at a concentration of 5 μM was found to have anti-tissue remodeling effects by significantly reducing a-SMA, fibronectin, and collagen type I. Apigenin inhibited the phosphorylation of MAPK (p38, JNK) induced by TGF-β1 and inhibited the production of ECM by blocking the transcription factor NF-κB pathway. We confirmed that the MAPK pathway regulates NF-κB by acting upstream of NF-κB through the specific antibodies of MAPK (SB203580, SP600125) and confirmed that myofibroblast differentiation and ECM synthesis are activated through this series of processes.Activated fibroblast, or a myofibroblast, has mobility and collagen contractile activitiesThis functional role of the myofibroblast induces tissue remodeling . Consequently, it is associated with pathogenesis of CRS. In the present study, we showed that treatment with apigenin suppressed enhancing cellular functions such as gel contraction and migration of nasal fibroblasts by TGF-β1, suggesting that apigenin has therapeutic potential for treatment of CRS.aniseeds. aniseed can reduce morphine dependence. This functional role of the myofibroblast induces tissue remodeling . Consequently, it is associated with pathogenesis of CRS. thereupon treatment with apigenin suppressed enhancing cellular functions such as gel contraction and migration of nasal fibroblasts by TGF-β1, suggesting that apigenin has therapeutic potential for treatment of CRS.
Pharmacological effect of this product from the perspective of traditional medicine: Headaches and sinusitis have a cold origin and come from drinking cold drinks or foods. This is because a very large group of diseases is caused by eating and drinking Cold foods, which causes phlegm to spread. . Eating cold foods and drinks can cause headaches, and if the cold stays in the head and does not come out, it can cause phlegm to accumulate in the head. As a result of the headache, it comes from the back of the head, and the cold and phlegm peak, and the whole head feels heavy and painful. And if and dont give treatment, it will look like a migraine headache. In this type, even if a person sleeps more, he gets more headaches. Because "sleep" is cold and with the continuation of sleep, the cold and phlegm of the head increases and when he wakes up, he has a more severe cold. The "cold" smells, like the smell of vinegar, aggravate his headache, and with headache gradually becomes "nauseous." In this type of headache, you can use "honey" in the fasting state, eating half a teaspoon of "Espand" in the evening, or eating a teaspoon of "cumin" in the evening. Also, at night, when you sleep, inhale the scent of roses from 40 to 120 days, which is one of the best treatments
References: 1-PubMed/Potential Effect and Mechanism of Action of Topical Chamomile (Matricaria Chammomila L.) Oil on Migraine Headache: A Medical Hypothesis /2014 2-Pmc/Review of Pharmacological Properties and Chemical Constituents of Pimpinella anisum/2012 3-Pmc/Apigenin alleviates TGF-β1-induced nasal mucosa remodeling by inhibiting MAPK / NF- kB signaling pathways in chronic rhinosinusitis/2018








User comments